A Guide to Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics is one area where it is essential to master the basics and then innovate with a solid foundation in place. We are walking through the basic principles of reverse logistics.
In an ideal world, you’d only ever ship products to your customers. However, as an eCommerce professional, the reality is you’ll inevitably have to reverse that flow for various reasons. But by mastering reverse logistics, you can save costs, boost customer satisfaction, and improve your bottom line.
A traditional supply chain starts with the warehouse or manufacturer and moves to the retailer or customers. Reverse logistics means products move from the customer to a relevant point in the supply chain.
Most often, you’ll think of returns (every seller’s nightmare). No one wins when returns are involved; customers are unhappy, retailers lose money, and inventory is tied up. While unavoidable, returns are also vital to build trust in an eCommerce store.
However, reverse logistics encompass more than returns. If you run a warranty or refund program, have to repair a product, rent items, or even offer sustainability programs, you’ll have products shipped to you. As such, this process is foundational to customer service and relationship management.
In this article, we’ll go through the basic principles of reverse logistics and how you can efficiently and profitably navigate the opposing flow of goods.
What are reverse logistics?
Goods can move backwards in the supply chain for a number of reasons, the most common being a customer return. According to Shopify, consumers return 14.5% of all eCommerce sales, but that’s only one component of reverse logistics. Other elements include:
- Returns management: Handling customer returns due to defects, damage, or dissatisfaction. Returns must be processed, returned to stock, or discarded or recycled as necessary.
- Rental management: If you provide rentals or temporary product try-outs, you need robust reverse logistics to handle returned items and prepare them for delivery to a new customer.
- Refurbishment & repair: Stores increasingly offer repairs and warranties as well as opportunities to purchase secondhand goods. These products must be processed and shipped to the appropriate point in the supply chain (such as back to the manufacturer for repair). If you launch this type of program, you need to incorporate warranty management.
- Recycling and disposal: Sustainability is a hot topic, and reverse logistics allow you to process returned products for proper recycling or disposal. Look into recycling and disposing of items that you can’t resell. You could also launch a program where customers send back old products (typically electronics) for sustainable disposal when they buy a new one.
Due to the variety of reasons for returns, products that are sent back must be sorted and processed into categories for reselling, recycling, repair, repackaging, or disposal.
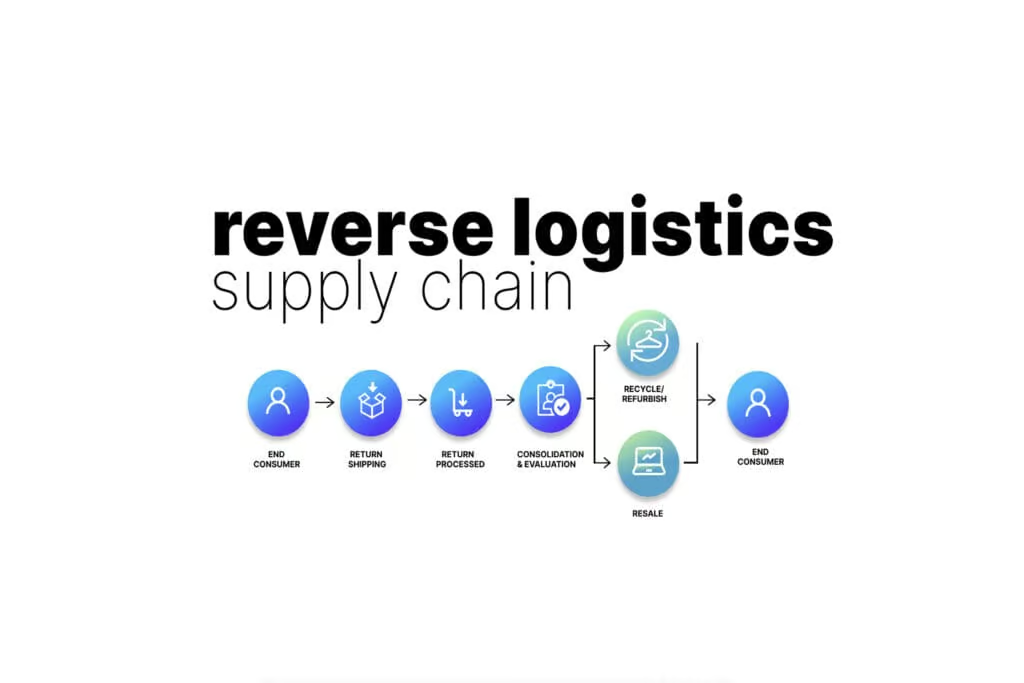
Reverse logistics flow
Reverse logistics differ for every company and are tailored to product offering and supply chain capabilities. For example, cosmetic companies like Ulta can’t resell returned items because they could be opened or used, which compromises the products’ integrity and safety. This makes the reverse supply chain for many health and beauty products a short process: Once an item is returned, they simply dispose of it.
On the other hand, furniture companies have greater complexities, so the product evaluation stage is critical for them. A couch that’s sent back to Pottery Barn, for instance, could have a small defect that disqualifies it for resale at a retail store but may be resold at a Pottery Barn outlet.
Your reverse logistics system has to process the inbound shipment, establish a review procedure, and then mark where the item needs to go next. From there, it should send the product to its designated destination, with tracking included to provide clarity and transparency to the customer.
Creating a reverse logistics flow that accurately details all avenues for returns not only secures operational efficiencies but also benefit your business and aligns with its values and goals.
Well-designed reverse logistics efficiently manage the return of goods from customers back to the seller or manufacturer, ensuring minimal cost, maximum value recovery, and customer satisfaction. Here’s an outline for a good structure:
- Request and authorization: Include authorization as well as reasons for returns to make processing and sorting easier (e.g., product defect, dissatisfaction, wrong size).
- Collection and transportation: All products should be returned to a single address. Typically, 3PLs provide options to have customers ship goods back to their dock area with prepared shipping labels that are only billed when used.
- Receipt and inspection: Manual inspection and logging of returned products is nonnegotiable. At this stage, acknowledge receipt of the return, which is important for resellable items (but less so for those designated for disposal). That should then trigger an automatic refund or repayment of deposit for the customer. This segment should also include: some text
- Determination of the returned product’s quality
- Sorting based on its next destination (disposal, repair, recycling, resale, repackaging, etc.)
- Distribution of products where they need to go (e.g, back to manufacturing or to repackaging)
- Reintegration or disposal: This is when the item is repaired, maintained, repackaged, disposed of, or recycled, as decided in the previous step. Once completed, the product should be added back into inventory when applicable.
To improve customer service, you can automate this process and track goods as they move through it. For example, communicate to buyers when their repair requests are received and what stage they’re in.
The 5 Rs of reverse logistics
The 5 Rs are foundational to reverse supply chains and will help you make decisions on how best to handle your logistics.
1. Returns and exchanges
Returns and exchanges are one of the most common cases in reverse logistics. Customers send back products for many reasons like poor fit or the product not meeting expectations. Some regions and platforms require you to accept returns for any reason within a certain window. Others, though, give you the freedom to decide how long and under what circumstances you’ll accept returns. Your return policy can therefore greatly impact customer trust, so it’s important to craft it with care and stick to it. Additionally, be sure to:
- Develop a simple return form where customers explain why they’re sending back their purchase.
- Reduce the costs of returns by including shipment labels in your product packaging.
Then, establish infrastructure to handle returns:
- Arrange for reverse logistics services with your 3PL.
- Set up a uniform inbound reverse logistics processing and policies, similar to the flow discussed earlier.
- Track returned goods in your system so you can stay on top of expenses. Be aware, it’s not always cost-effective to accept returns; if processing is expensive and the cost of the product is low, simply offering a refund and letting the customer keep the item may be more beneficial to your bottom line.
2. Reselling returned products
Once returned, you can add many products back into your inventory, whether they’re returns, refurbished items, or restored rentals.
Reselling these goods is an excellent strategy to draw in new customers. For instance, Nordstrom Rack allows shoppers who may not want to pay retail prices to interact with the Nordstrom brand. Meanwhile, the clothing brand KILLSTAR runs their Resurrect program, which lets customers resell their used brand items (with the goal to promote sustainability).
One of the difficulties of reselling goods is reintroducing them into your inventory, which entails deciding if you’ll sell them as “new,” “like new,” “used,” etc. You also have to determine if those items require repackaging. Then, you’ll need a system to carry out next steps, including scanning products back into inventory and storing them correctly in your warehouse.
3. Repairs and maintenance
Repairs and maintenance are tricky because they typically require sending products all the way back to the start of the supply chain: the manufacturer. In addition, you’ll need tooling to track the progression and location of each item throughout that cycle, as customers often want to follow the movement of their product.
Providing free or low-cost repairs can be an effective way to lower the volume of products in a reverse logistics flow. Lululemon capitalizes on this by offering free hemming on all tops and pants, which lessens the number of returned items due to poor fit. Most electronics follow suit, with brands like Anker and Fairphone giving long-term guarantees and repairs.
Your repair progression has to include:
- Inspecting the product when it comes back into the warehouse to verify the issue
- Processing the return and forwarding it to the repair point or manufacturer
- Tracking items throughout the process, since they have to return to the customer (that means scanning products into and out of each point so you can easily send buyers updates and automatic alerts)
- Sending the repaired product back to the customer, which can be difficult if your manufacturer is in China and shipping directly to the customer could result in unplanned duties or customs fees. You’ll have to review and optimize that route to reduce costs and timelines.
Of course, not all repairs result in sending products back to the customer. Instead, you may repair your product, repackage it, then return it to inventory, which diminishes the need for tracking.
4. Recycling and disposal
Recycling and disposal applies when a product is either too damaged to return to inventory, or you allow customers to send in damaged products for sustainable disposal. For example, Fairphone lets customers who buy a new phone send their old one in for recycling. This process requires an inbound system that directs products to either the manufacturer for disassembly and recycling or a sustainable disposal site.
Proper recycling and disposal of items in reverse logistics is not only important for cost savings but also for the environment. Take H&M, which resells clothes secondhand or turns them into other textile products to cut down on waste.
5. Replacements
In some cases, you’ll simply want to replace a product. You still need to decide whether to let the customer keep it, repair it and return it to inventory, etc., but you then follow up by sending the buyer a new item.
Replacements are also an easy way to bypass the more complicated aspects of reverse logistics. This option works well if your product costs are low compared to those of shipping, inspection, and reintegration. Here, you simply offer a replacement item, free of charge, without requiring the customer to send you the defective one. In most cases, that entails setting up a digital returns process to receive photo evidence of damage and then ship a new item to the customer.
The importance of data in reverse logistics
Data drives eCommerce and logistics, and that includes reverse flows. You need information to understand trends, why shoppers return products, how much your reverse logistics cost, which types of returns your business normally handles, and more. That, in turn, promotes robust forecasting, planning, and cost optimization. For instance, if you discover you frequently take on repairs, you can determine if it’s more cost-effective to establish a repair shop in a given region to reduce timelines and expenses.
You’ll also need software to support transparency throughout your chain (if products have to go back to buyers, they want to see the movement). Good software can also help you automate processes, which provides insights at every step and cuts costs as you move items from return to inspection to repackaging, recycling, or repair.
Reverse logistics can be intimidating and nuanced. Establish a solid procedural flow and determine how your business will handle items in each of the above-mentioned scenarios to build a smooth process that satisfies your buyers and supports a thriving business.
Related articles
-
Warehouse Management Best Practices: 5 Tips for Optimized Processes
Read moreWarehouses are the heart of many companies, but operations can be difficult to manage. Continual improvement is the best approach to overcoming this challenge. In this article, we’ll discuss the industry’s best practices for warehouses.
-
Prevent Stockouts: 5 Ways to Avoid Going out of Stock
Read morePlenty of businesses have been missing out due to out-of-stock issues over the last few months. So how can you avoid losing money because of out-of-stock problems? One of the best ways is by implementing technology that fosters visibility.
-
8 Effective Ways to Offer Free Shipping
Read moreAmid all the talk of recession and the eye-popping statistics on inflation, many businesses are turning to a strategic focus: customer retention. There are many ways to do this, but one that quickly comes to mind is shipping experience.



